The discovery of the DarkCloud Stealer malware has set off alarm bells across the cybersecurity landscape, spotlighting a formidable threat to governments and financial sectors alike. Uncovered by researchers from Palo Alto Networks in a recent series of cyberattacks, this sophisticated malware is adept at circumventing traditional defense mechanisms. With its inception traced back to earlier sightings, DarkCloud Stealer has undergone a significant transformation, embracing advanced tactics like AutoIt scripting and multi-stage payload dissemination. Its primary aim is the extraction of sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card details, and crucial browser data, thereby escalating concerns within high-tech, governmental, and financial institutions.
Sophisticated Malware Tactics Unveiled
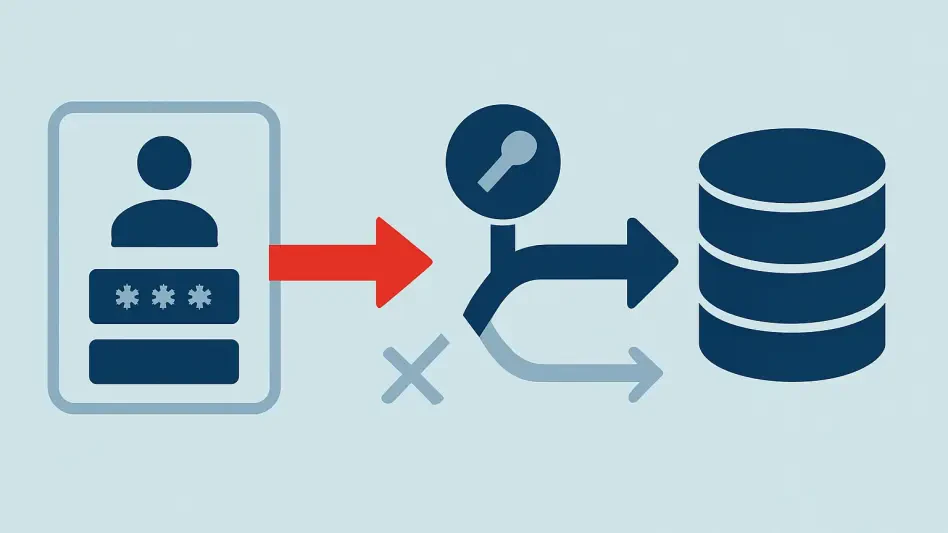
The propagation of DarkCloud Stealer largely hinges on misleading phishing emails that lure unsuspecting users with deceptive RAR archives or PDF files. These files, once opened, coax users into downloading compromised archives masquerading as routine software updates, typically hosted on platforms like files.catbox.moe. Upon execution, these RAR archives deliver an AutoIt-compiled Portable Executable (PE) file, effectively acting as a dropper for the malware. By employing encrypted shellcode and XORed payloads, DarkCloud Stealer complicates static analysis efforts, thereby evading detection with relative ease. The malware’s infection chain is built on a multi-layered approach, utilizing complex functions such as VirtualProtect() and CallWindowProc() to deploy its payload. This intricate structure confers extensive data-stealing capabilities, seeking information from browser credentials, email client data, FTP/SMTP logins, and sensitive credit card details.
The advanced evasion techniques integrated within DarkCloud Stealer include anti-analysis measures that identify and nullify debugging tools like WinDbg and Wireshark. In its pursuit of persistence, the malware leverages the Windows RunOnce registry key, ensuring its continued presence on infected systems. The multi-faceted delivery and execution of this malware demonstrate a high level of sophistication, posing a significant challenge to conventional security layers.
Heightened Threat Environment
The threat of DarkCloud Stealer is exacerbated by its use of public IP geolocation services and command-and-control (C2) communication. This sophisticated interface facilitates the theft and transfer of data from compromised systems, making it a potent menace. Observations by Palo Alto Networks have revealed an alarming increase in detected samples, particularly targeting government entities. In response to the evolving threat landscape, the organization has fortified its cybersecurity solutions, including Cortex XDR and Advanced WildFire, to combat these advanced strategies. These solutions incorporate behavioral and machine learning-based detection mechanisms, elevating the defensive capabilities against such elusive threats.
Entities are urged to maintain heightened vigilance, implementing robust security protocols to detect and mitigate these complex intrusions. Additionally, Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) have been made available to aid in the identification and neutralization of DarkCloud Stealer-infested systems. The growing sophistication of cyber threats like DarkCloud Stealer underscores the necessity for continual updates and enhancements to current security frameworks to effectively shield organizations from this sophisticated and rapidly evolving form of malware.
A Call to Strategic Action
The emergence of DarkCloud Stealer malware has sent shockwaves through the cybersecurity realm, highlighting a grave threat to both governmental entities and financial sectors. Palo Alto Networks researchers recently uncovered this sophisticated malware during a spate of cyberattacks, revealing its adeptness in dodging traditional security systems. Originating from prior detections, DarkCloud Stealer has evolved with advanced tactics, including AutoIt scripting and multi-phase payload distribution. Its primary focus is extracting sensitive data like login credentials, credit card details, and vital browser information, heightening alarms within technology-driven, governmental, and financial institutions. This malware’s evolution underscores the pressing need for enhanced security measures to counteract its growing threat, as it targets critical information that could have far-reaching implications for affected sectors, potentially posing severe risks to their operational integrity and financial stability.